Page 311 - Praxair - Specialty Gases and Equipment Reference Guide
P. 311
Flowmeters
Overview
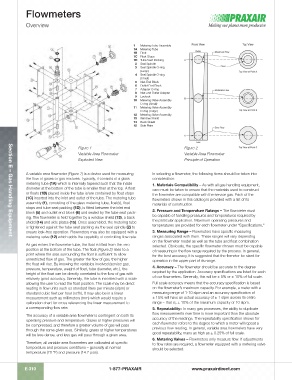
1 Metering Tube Assembly
1A Metering Tube
1B Float
1C Float Stops
1D Tube Seat Packing
2 Seal Spindle
3 Seal Spindle O-ring
(Large)
4 Seal Spindle O-ring
(Small)
5 Inlet End Block
6 Outlet End Block
7 Adapter O-ring
8 Inlet and Outlet Adapter
9 Locknut
10 Metering Valve Assembly
O-ring (Small)
11 Metering Valve Assembly
O-ring (Large)
12 Metering Valve Assembly
13 Window Shield
14 Back Shield
15 Side Plate
Figure 1 – Figure 2 –
Variable Area Flowmeter Variable Area Flowmeter
Exploded View Principle of Operation
A variable area flowmeter (Figure 1) is a device used for measuring In selecting a flowmeter, the following items should be taken into
the flow of gases or gas mixtures. Typically, it consists of a glass consideration:
metering tube (1A) which is internally tapered such that the inside 1. Materials Compatibility – As with all gas handling equipment,
diameter at the bottom of the tube is smaller than at the top. A float care must be taken to ensure that the materials used to construct
or floats (1B) placed inside the tube is/are contained by float stops the flowmeter are compatible with the service gas. Each of the
(1C) inserted into the inlet and outlet of the tube. The metering tube flowmeters shown in this catalog is provided with a list of its
assembly (1), consisting of the glass metering tube, float(s), float materials of construction.
stops and tube seat packing (1D), is fitted between the inlet end
block (5) and outlet end block (6) and sealed by the tube seat pack- 2. Pressure and Temperature Ratings – The flowmeter must
ing. The flowmeter is held together by a window shield (13), a back be capable of handling pressures and temperatures required by
shield (14) and side plates (15). Once assembled, the metering tube the particular application. Maximum operating pressures and
is tightened against the tube seat packing via the seal spindle (2) to temperatures are provided for each flowmeter under “Specifications.”
ensure leak-free operation. Flowmeters may also be equipped with a 3. Measuring Range – Flowmeters have specific measuring
metering valve (12) which adds the capability of controlling flow rate. ranges associated with them. These ranges will vary depending
Section E – Gas Handling Equipment
As gas enters the flowmeter tube, the float is lifted from the zero on the flowmeter model as well as the tube and float combination
selected. Obviously, the specific flowmeter chosen must be capable
position at the bottom of the tube. The float (Figure 2) rises to a of measuring in the flow range required by the process. In general,
point where the area surrounding the float is sufficient to allow for the best accuracy, it is suggested that the flometer be sized for
unrestricted flow of gas. The greater the flow of gas, the higher operation in the upper part of its range.
the float will rise. By knowing the variables involved (service gas,
pressure, temperature, weight of float, tube diameter, etc.), the 4. Accuracy – The flowmeter should be accurate to the degree
height of the float can be directly correlated to the flow of gas with required by the application. Accuracy specifications are listed for each
relatively good accuracy. Generally, the tube is inscribed with a scale of our flowmeters. Generally, this will be ± 5% or ± 10% of full scale.
allowing the user to read the float position. The scale may be direct Full scale accuracy means that the accuracy specification is based
reading in flow units such as standard liters per minute (slpm) or on the flowmeter’s maximum capacity. For example, a meter with a
standard cubic feet per hour (scfh). It may also be in a linear measuring range of 1-10 slpm and an accuracy specification of
measurement such as millimeters (mm) which would require a ± 10% will have an actual accuracy of ± 1 slpm across its entire
calibration chart for cross referencing the linear measurement to range – that is, ± 10% of the maximum capacity of 10 slpm.
a corresponding flow rate. 5. Repeatability– In many gas processes, the ability to duplicate
The accuracy of a variable area flowmeter is contingent on both its flow measurements over time is more important than the absolute
operating pressure and temperature. Gases at higher pressures will accuracy of the readings. The repeatability specification shown for
be compressed, and therefore a greater volume of gas will pass each flowmeter refers to the degree to which a meter will repeat a
through the same given area. Similarly, gases at higher temperatures previous flow reading. In general, variable area flowmeters have very
will be less dense, and less gas will pass through a given area. good repeatability, many as high as ± 0.25% of full scale.
Therefore, all variable area flowmeters are calibrated at specific 6. Metering Valves – Flowmeters only measure flow. If adjustments
to flow rates are required, a flowmeter equipped with a metering valve
temperature and pressure conditions – generally at normal should be selected.
temperature (70 °F) and pressure (14.7 psia).
E•310 1-877-PRAXAIR www.praxairdirect.com